It is important to ensure that all the latest patches and updates are applied to any Windows Server 2003 (WS2003) installations if the server will continue to be used past the official July 14, 2015, end-of-life, which is when Microsoft ceased supporting the software.
I have the latest windows update agent, IE8(with the latest cumulative update),TLS 1.0 enabled SSL 2.0 and 3.0 disabled, still the probelm never goes away I would really like to get it working as im going to migrate my site from xp to server 2003 and i want to be upto date on it.
WS2003 contains a number of features to help manage patches.
The Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) helps manage patches for several products. It has a section devoted to Windows Server 2003. It uses a repository of Windows updates to check systems for updates and packages. It can either send notifications of missing updates and patches or install them automatically. It also includes features to allow users to automatically install some classes of updates and manually install others.
Another important tool is the Microsoft Security Baseline Analyzer. It scans for missing security patches and common security misconfigurations in Windows Server systems.
Standalone updates are applied to a computer that is already running the operating system. When the update program is run it installs the necessary files and makes the appropriate registry changes. Update.exe registers the updates under the following registry keys:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftUpdatesServer2003SP2KB######
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionHotfixKB######
How to install updates on multiple systems
To install updates on multiple systems, follow these steps:
- Connect to the network where you want to create the distribution folder.
- In the shared distribution folder, create a folder for the update files.
- Copy the Windows Server 2003 Update.exe program to the distribution folder you created in Step 2.
- To install the update from the distribution folder, run the WindowsServer2003-KB######-x86-LLL.exe program.
- Restart your computer after you finish installing all of the updates.
For more detailed information on installing updates, see Microsoft’s guide titled Installing and Deploying Updates for Microsoft Windows Server 2003.
Note: Not all patches, or fixes, that are intended to resolve one or two vulnerabilities, work flawlessly with all installations. Some patches might break parts of the system, or have other undesirable consequences, so it is important to check patches before applying them to all the servers in an installation. This is frequently done by setting up a test system, either a virtual copy of the server configuration or a separate test server, and testing the patches.
If there is a problem with a patch, it can be removed by going to the Control Panel and then selecting Add or Remove Software. Make sure “Show Updates” is checked then click on the update and click on “remove.”
As an alternative to the Microsoft supplied programs, or as a supplement, you can use a third-party patch manager like ManageEngine from Desktop Central to manage Windows and non-Windows patches.
2015 patches for Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003 Sp2 X64
Here are some of the recently released 2015 patches for Windows Server 2003. Make sure they are all applied as soon as possible.
“GsDraw error (1): GenericError” — This fix is for when an error occurs and the application crashes when text outline is created in Windows.
MS15-057 — This vulnerability could allow remote code execution if Windows Media Player opens specially crafted s this vulnerability could take complete control of an affected system remotely.
MS15-061 — This patch resolves vulnerabilities that could allow elevation of privilege if an attacker logs on to the system and runs a specially crafted application. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts that have full user rights.
MS15-044 and MS15-051 — This patch prevents remote code execution if a user opens a specially crafted document or goes to an untrusted webpage that contains embedded TrueType fonts. Without this patch, a cracker could elevate privileges via local logon and run arbitrary code in kernel mode. They could then possibly install programs, alter or delete data and create new accounts.
Check out this article to learn more about how GoDaddy handled the Windows 2003 server end-of-life.
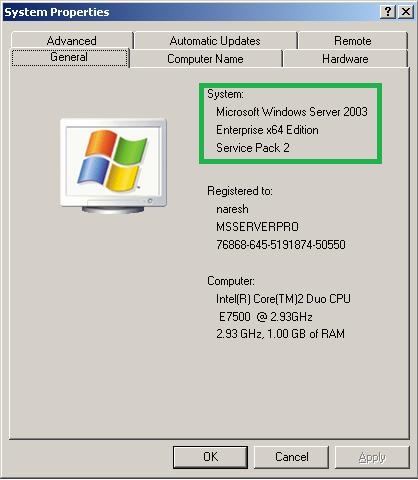

Image by: dotty finlow via Compfightcc
Because of the nature of the Windows Service pack (SP) releases, all the windows updates are consumed by SP upgrade. So once you upgrade to a new SP all the updates that were installed earlier cannot be uninstalled. Since Windows PowerShell is released as an update to Windows, upgrading to W2k3 SP2 will remove the powershell uninstaller and you cannot uninstall PowerShell directly.
Windows update technology do not support out of order uninstalls ie.,
1. Install Update A + Install Update B + Install Update C.
2. To uninstall Update A, the supported way to uninstall A is -> Uninstall C + Uninstall B then Uninstall A.
Since W2K3 SP2 is an update to W2K3 SP1, if you install Powershell on W2K3 SP1 and upgrade to W2K3 SP2, to uninstall PowerShell you first have to uninstall W2K3 SP2.
Windows Server 2008 Sp2
I just want to let you all know of this Windows Update behaviour.
Windows Server 2003 Sp2 Update Download
Krishna Vutukuri[MSFT]
Windows PowerShell Development
This posting is provided “AS IS” and confers no rights or warranties.
Update: PowerShell uninstaller is present on disk after upgrading to W2K3-SP2 at %windir%$ntuninstallkb926139$spuninstallspuninstall.exe. Windows update technology do not support out of order uninstalls, see “Removing Windows software updates in the wrong order may cause the operating system to stop functioning” (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/823836/en-us).